
The other authors declared no competing interests. Funding Information: TFH has received research funding from AstraZeneca and GlaxoSmithKline. KP is supported by the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research Health Professional-Investigator Program award and the Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit. DJC is supported by Australian Government Prestigious International Research Tuition Scholarship (PIRTS) and University Postgraduate Research Scholarship (UPRS). The Sabah malaria research program is supported by US National Institutes of Health (R01 AI116472–03). Note = "Funding Information: This work was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (grant numbers 10373156 fellowships to NMA, BEB, and MJG ) and Improving Health Outcomes in the Tropical North: A multidisciplinary collaboration “Hot North” (grant 1131932) and the Australian Centre of Research Excellence in Malaria Elimination. Studies using surrogate baseline creatinine values should report specific methodology.",

Preferred alternatives include MDRD equation back-calculation with a population mean GFR, age- and sex-specific GFR values corrected for “good health,” or lowest measured creatinine. MDRD back-calculation using a cohort mean GFR showed low total error (22%) and an AUC ROC of 0.85. Conclusion: Current methods for estimating baseline creatinine are large sources of potential error in acute infection studies. Back-calculation using MDRD and assumed GFR of 100 ml/min, age and sex-reference GFR values adjusted for good health, and lowest creatinine during admission performed similarly, best predicting AKI incidence (area under the receiver operating characteristic curves of 0.85, 0.87, and 0.85, respectively). Back-calculation with CKD-EPI and GFR of 100 ml/min most accurately predicted AKI but misclassified all AKI stages and had low levels of agreement with true AKI diagnoses. Back-calculated distributions were performed using GFRs of 75 and 100 ml/min.Results: All equations using an assumed GFR of 75 ml/min underestimated AKI incidence by more than 50%.
Known AKI incidence (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes criteria) was compared with AKI incidence classified by (1) back-calculation using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equation with and without a Chinese ethnicity correction coefficient (2) back-calculation using the Chronic Kidney Disease–Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation (3) assigning glomerular filtration rate (GFR) from age and sex-standardized reference tables and (4) lowest measured creatinine during admission.
AGE BACKCALCULATION CORRECTIONS FOR TRIAL
Studies using surrogate baseline creatinine values should report specific methodology.Ībstract = "Introduction: Classification of acute kidney injury (AKI) requires a premorbid baseline creatinine, often unavailable in studies in acute infection.Methods: We evaluated commonly used surrogate and imputed baseline creatinine values against a “reference” creatinine measured during follow-up in an adult clinical trial cohort. MDRD back-calculation using a cohort mean GFR showed low total error (22%) and an AUC ROC of 0.85.Ĭurrent methods for estimating baseline creatinine are large sources of potential error in acute infection studies.
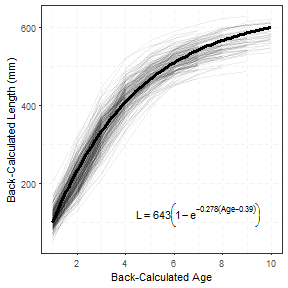
Back-calculated distributions were performed using GFRs of 75 and 100 ml/min.Īll equations using an assumed GFR of 75 ml/min underestimated AKI incidence by more than 50%. We evaluated commonly used surrogate and imputed baseline creatinine values against a “reference” creatinine measured during follow-up in an adult clinical trial cohort.

Classification of acute kidney injury (AKI) requires a premorbid baseline creatinine, often unavailable in studies in acute infection.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
